Publications
2024 , 2023 , 2022 , 2021 and older
Topology-Preserving Downsampling of Binary Images
Chia-Chia Chen and Chi-Han Peng
The 18th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2024
Paper (preprint) | Project page | Video | Code
Abstract:
We present a novel discrete optimization-based approach to generate downsampled versions of binary images that are guaranteed to have the same topology as the original, measured by the zeroth and first Betti numbers of the black regions, while having good similarity to the original image as measured by IoU and Dice scores. To our best knowledge, all existing binary image downsampling methods don’t have such topology-preserving guarantees. We also implemented a baseline morphological operation (dilation)-based approach that always generates topologically correct results. However, we found the similarity scores to be much worse. We demonstrate several applications of our approach. First, generating smaller versions of medical image segmentation masks for easier human inspection. Second, improving the efficiency of binary image operations, including persistent homology computation and shortest path computation, by substituting the original images with smaller ones. In particular, the latter is a novel application that is made feasible only by the full topology-preservation guarantee of our method.
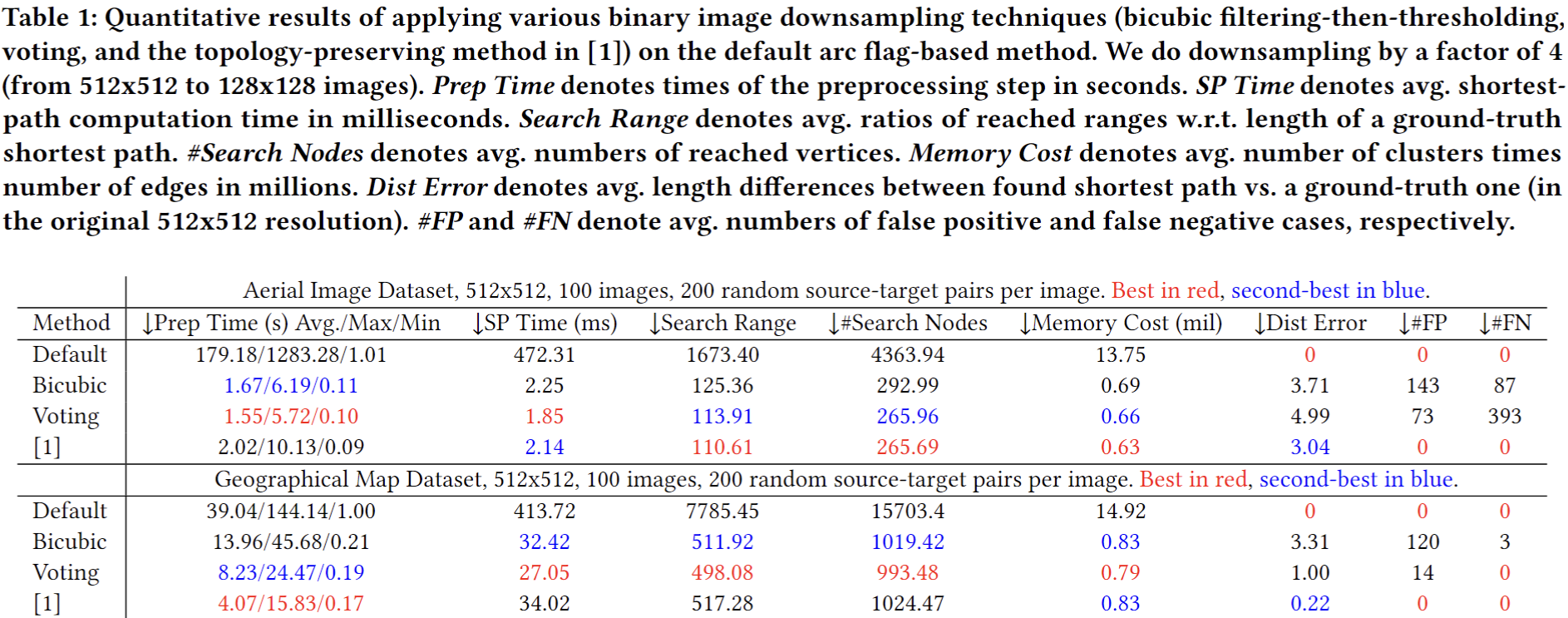
Shortest Path Speed-up Through Binary Image Downsampling
Chia-Chia Chen and Chi-Han Peng
Siggraph Asia 2024 Poster
Paper (preprint) | Poster
Abstract:
We propose a novel approach to achieve huge speed-ups for shortest path computations on 2D binary images at the cost of slight inaccuracies. This is done by migrating the arc flag-based shortest path methods, which can deliver large speed-ups for run-time shortest path computations but needed a computationally expensive preprocessing step, to work on downsampled versions of the input images. Through extensive tests, we found that our approach hugely reduces the costs of the preprocessing step, therefore resolved a performance bottleneck of the arc flag-based methods.
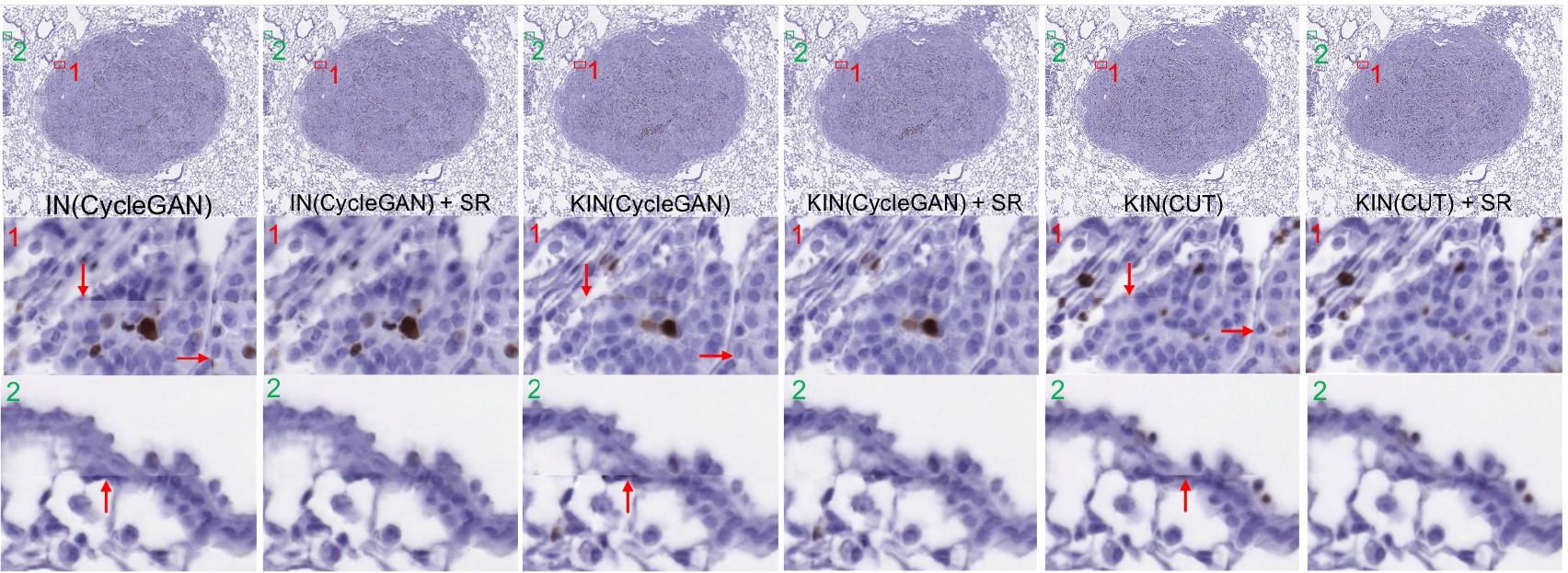
Seam Removal for Patch-Based Ultra-High-Resolution Stain Normalization
Chi-Chen Lee and Chi-Han Peng
The 23rd IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE) 2023
Paper | Video |
Abstract:
Stain normalization is a key computational method in pathology that transforms histological stain images of one style to another. Modern methods are mostly based on neural image-to-image translation techniques. For very large image inputs, which are common in practice (e.g., whole slide images (WSIs)), the inferences are forced to run multiple times, each on a different subset of the image, due to GPU memory constraints. To minimize the differences between different outputs, several modifications of the standard instance-normalization (IN) layers have been proposed. Despite the reduced color variances, visible seams remain even with these approaches, which are disruptive to histologists when they closely examine the stitched results. These seams are also detrimental to the performance of some downstream tasks such as tumor classification. Hence, we propose a novel approach to effectively remove the seams by utilizing a Pix2Pix-based neural network and an alpha blendingbased post-processing step. Tested on real-world medical and natural image datasets, we found that our method performed much better than traditional Poisson image editing-based seam removal approaches. Our approaches qualitatively (in terms of the visibility of the seams) and quantitatively improved the results by prior stain normalization methods by large margins.
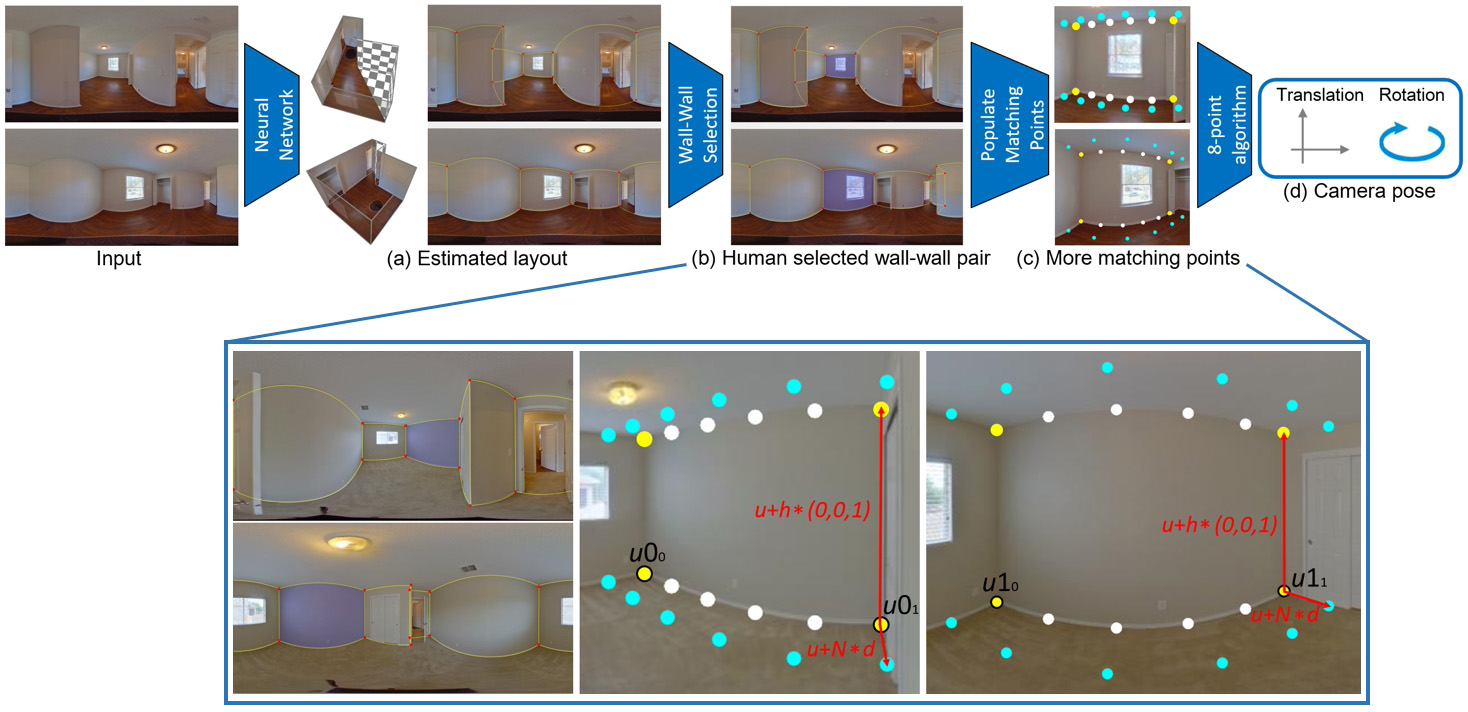
Interactive Relative Pose Estimation for 360◦ Indoor Panoramas through Wall-Wall Matching Selections
Bo-Sheng Chen and Chi-Han Peng
ACM Siggraph Asia 2023 Poster
Paper (preprint) | Poster | Supplementary Materials | Demo Program |
Abstract:
We present an interactive approach to estimating the relative camera pose of two panoramas shot in the same indoor environment. Compared to the trivial interactive baseline, which would require the user to precisely select 8 or more pairs of matching points by mouse clicks, our method just needs the user to select a pair of matching walls with two mouse clicks or keyboard strokes. Our method is based on the key observation that, in most cases, there exist at least one or multiple pairs of roughly matched walls in the room layouts estimated by neural networks - which alone are sufficient to generate accurate relative camera poses. Tested on a real-world indoor panorama dataset, our method outperforms current state-of-the-art automatic methods by large margins, compensating the additional human efforts. Through user studies, we found that matched wall-wall pairs can be easily recognized and selected by humans in relatively short time, indicating that such an interactive approach is practical.
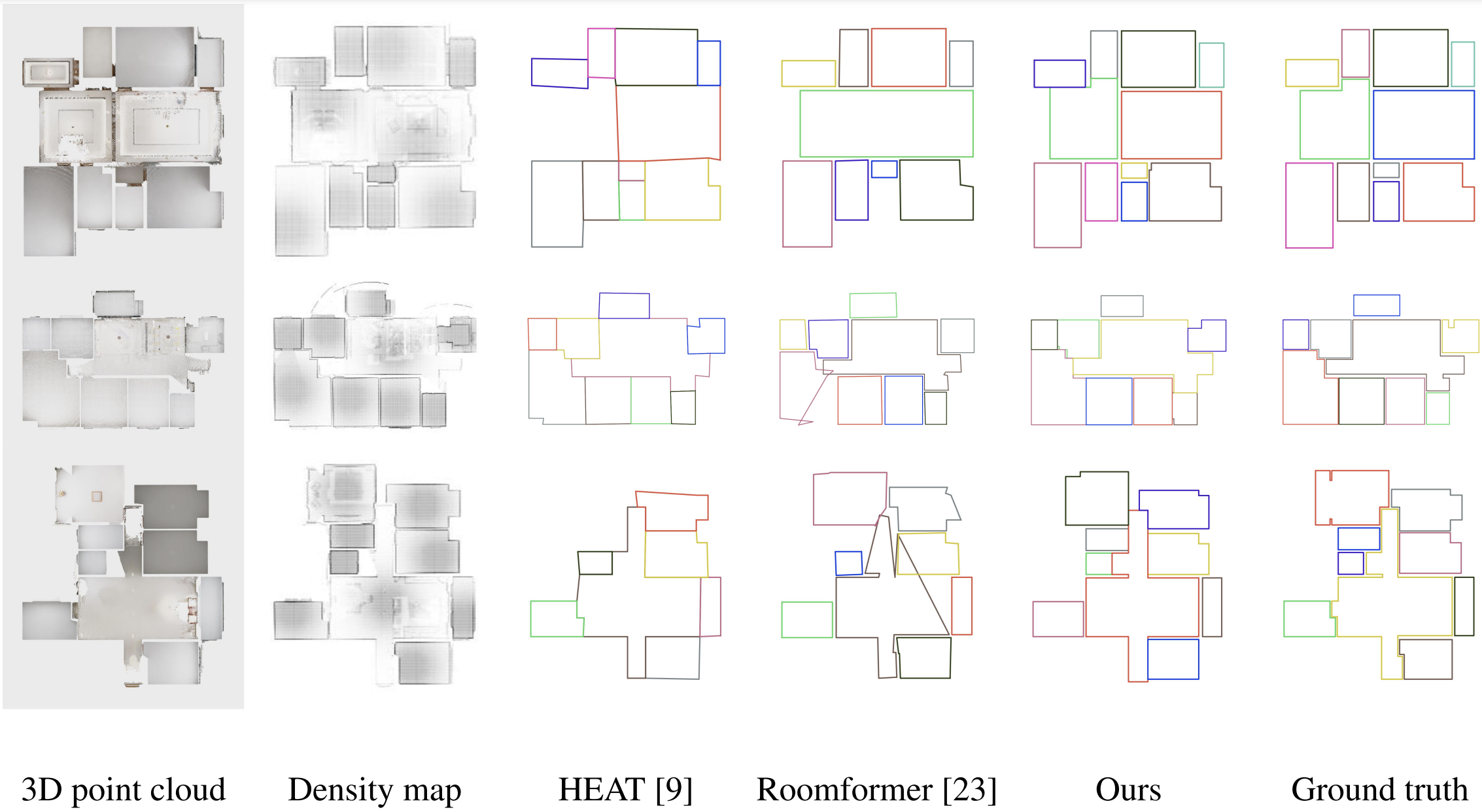
SLIBO-Net: Floorplan Reconstruction via Slicing Box Representation with Local Geometry Regularization
Jheng-Wei Su, Kuei-Yu Tung, Chi-Han Peng, Peter Wonka, Hung-Kuo Chu
Thirty-seventh Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2023
NeurIPS Proceedings page |
Abstract:
This paper focuses on improving the reconstruction of 2D floorplans from unstructured 3D point clouds. We identify opportunities for enhancement over the existing methods in three main areas: semantic quality, efficient representation, and local geometric details. To address these, we presents SLIBO-Net, an innovative approach to reconstructing 2D floorplans from unstructured 3D point clouds. We propose a novel transformer-based architecture that employs an efficient floorplan representation, providing improved room shape supervision and allowing for manageable token numbers. By incorporating geometric priors as a regularization mechanism and post-processing step, we enhance the capture of local geometric details. We also propose a scale-independent evaluation metric, correcting the discrepancy in error treatment between varying floorplan sizes. Our approach notably achieves a new state-of-the-art on the Structure3D dataset. The resultant floorplans exhibit enhanced semantic plausibility, substantially improving the overall quality and realism of the reconstructions. We will release code after publication.
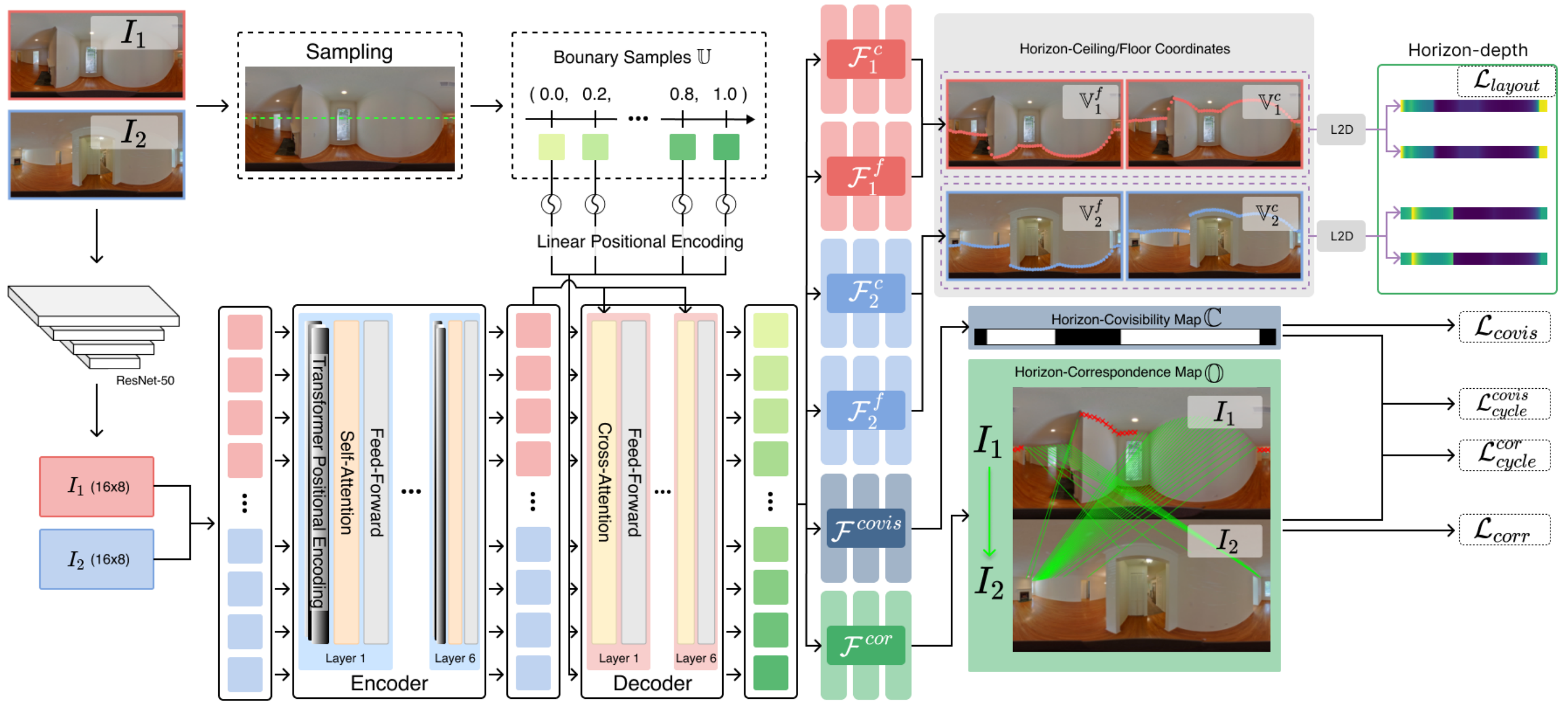
GPR-Net: Multi-view Layout Estimation via a Geometry-aware Panorama Registration Network
Jheng-Wei Su, Chi-Han Peng, Peter Wonka, Hung-Kuo Chu
IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2023,
Omnidirectional Computer Vision Workshop (Omnicv2023)
Paper (Arxiv) |
Abstract:
Reconstructing 3D layouts from multiple 360∘ panoramas has received increasing attention recently as estimating a complete layout of a large-scale and complex room from a single panorama is very difficult. The state-of-the-art method, called PSMNet, introduces the first learning-based framework that jointly estimates the room layout and registration given a pair of panoramas. However, PSMNet relies on an approximate (i.e., "noisy") registration as input. Obtaining this input requires a solution for wide baseline registration which is a challenging problem. In this work, we present a complete multi-view panoramic layout estimation framework that jointly learns panorama registration and layout estimation given a pair of panoramas without relying on a pose prior. The major improvement over PSMNet comes from a novel Geometry-aware Panorama Registration Network or GPR-Net that effectively tackles the wide baseline registration problem by exploiting the layout geometry and computing fine-grained correspondences on the layout boundaries, instead of the global pixel-space. Our architecture consists of two parts. First, given two panoramas, we adopt a vision transformer to learn a set of 1D horizon features sampled on the panorama. These 1D horizon features encode the depths of individual layout boundary samples and the correspondence and covisibility maps between layout boundaries. We then exploit a non-linear registration module to convert these 1D horizon features into a set of corresponding 2D boundary points on the layout. Finally, we estimate the final relative camera pose via RANSAC and obtain the complete layout simply by taking the union of registered layouts. Experimental results indicate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both panorama registration and layout estimation on a large-scale indoor panorama dataset ZInD.
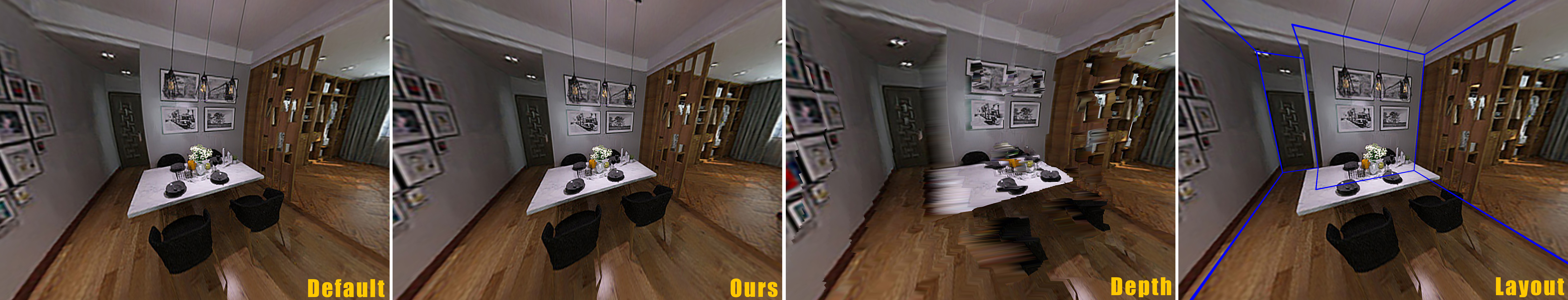
Distortion Reduction for Off-Center Perspective Projection of Panoramas
Chi-Han Peng, Jiayao Zhang, Chia-Chia Chen, Yun-Wei Lin
NICOGRAPH International 2023. *Best Short Paper Award
Paper | Video | Slides | Paper (previous Arxiv version) |
Abstract:
A key assumption of perspective projection is that linear features in 3D shall remain linear after being projected to the 2D screen. This assumption is preserved when we draw a spherical panorama perspectively in arbitrary viewing directions and field-of-views as long as the camera position is fixed at the center. However, when the camera moves away from the center, barrel-like distortions appear and such assumption breaks. To address this issue, we propose modifications to the equirectangular-to-perspective (E2P) projection that significantly reduced distortion of linear features when the camera position is away from the center. We compared with other common methods that aim to augment panoramas with 3D information including: 1) building a point cloud augmented with per-pixel depth and 2) building a 3D room model according to room layouts, and found that our method produced rendering results with less linearity distortion measured quantitatively and qualitatively.
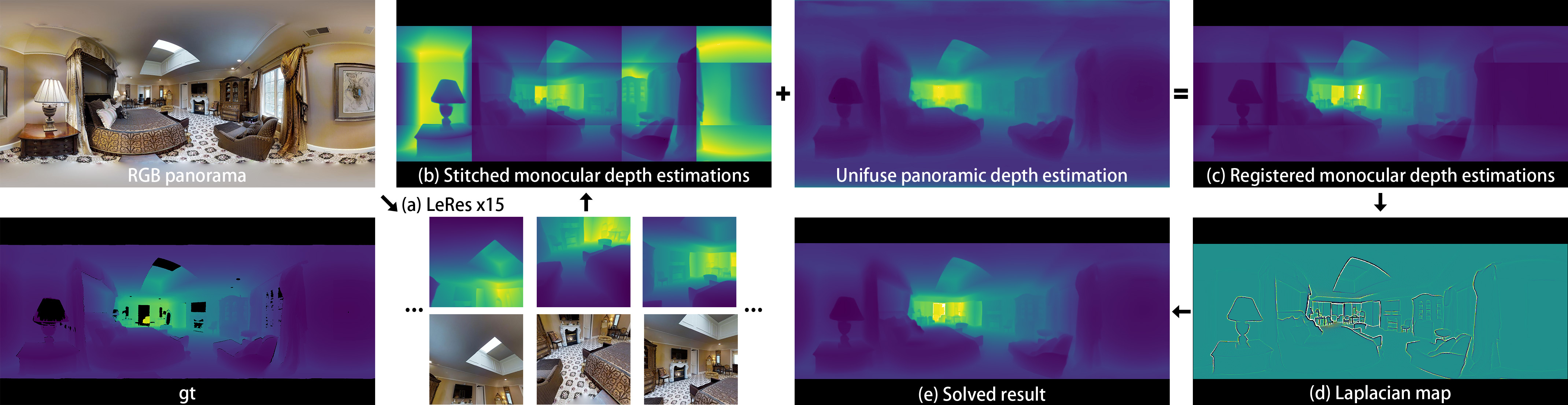
High-Resolution Depth Estimation for 360◦ Panoramas through Perspective and Panoramic Depth Images Registration
Chi-Han Peng and Jiayao Zhang
IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2023
Paper | Supplemental | Poster | Video | Code |
Abstract:
We propose a novel approach to compute high-resolution (2048x1024 and higher) depths for panoramas that is significantly faster and qualitatively and qualitatively more accurate than the current state-of-the-art method (360OMonoDepth). As traditional neural network-based methods have limitations in the output image sizes (up to 1024x512) due to GPU memory constraints, both 360OMonoDepth and our method rely on stitching multiple perspective disparity or depth images to come out an unified panoramic depth map. However, to achieve globally consistent stitching, 360OMonoDepth relied on solving extensive disparity map alignment and Poisson-based blending problems, leading to high computation time. Instead, we propose to use an existing panoramic depth map (computed in real-time by any panorama-based method) as the common target for the individual perspective depth maps to register to. This key idea made producing globally consistent stitching results a straightforward task. Our experiments show that our method generates qualitatively better results than existing panorama-based methods, and further outperforms them quantitatively on datasets unseen by these methods.
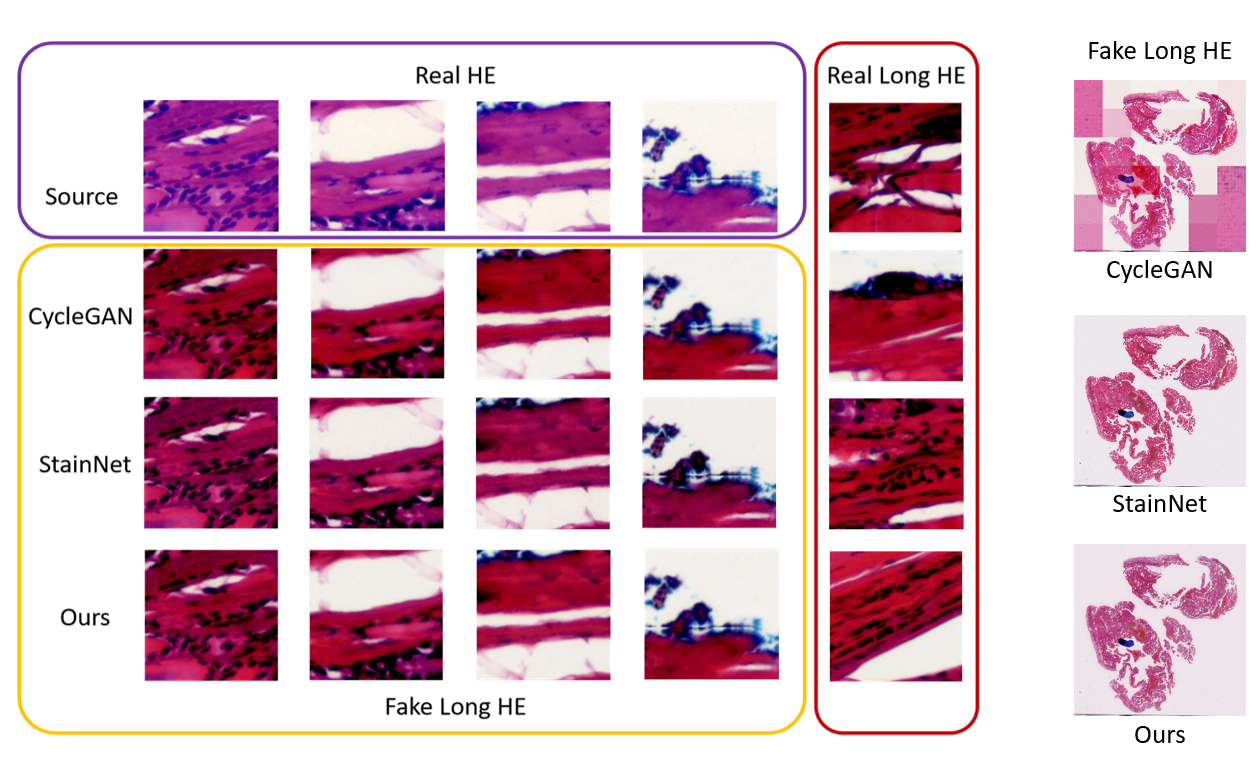
H&E Stain Normalization using U-Net
Chi-Chen Lee, Po-Tsun Paul Kuo, and Chi-Han Peng
IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioEngineering (BIBE), 2022 (short paper)
Paper | Arxiv |
Abstract:
We propose a novel hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain normalization method based on a modified U-Net neural network architecture. Unlike previous deep-learning methods that were often based on generative adversarial networks (GANs), we take a teacher-student approach and use paired datasets generated by a trained CycleGAN to train a U-Net to perform the stain normalization task. Through experiments, we compared our method to two recent competing methods, CycleGAN and StainNet, a lightweight approach also based on the teacher-student model. We found that our method is faster and can process larger images with better quality compared to CycleGAN. We also compared to StainNet and found that our method delivered quantitatively and qualitatively better results.
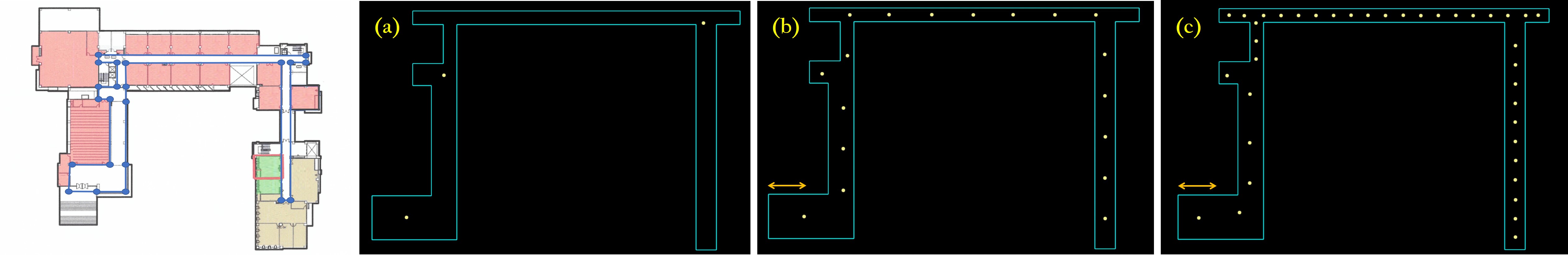
Optimizing Placements of 360◦ Panoramic Cameras in Indoor Environments by Integer Programming
Syuan-Rong Syu and Chi-Han Peng
Smart Tools and Applications in Graphics (STAG), 2022
Paper | Slides | Arxiv |
Abstract:
We propose a computational approach to find a minimal set of 360◦ camera placements that together sufficiently cover an indoor environment for the building documentation problem in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries. Our approach, based on a simple integer programming (IP) problem formulation, solves very efficiently and globally optimally. We conducted a study of using panoramas to capture the appearances of a real-world indoor environment, in which we found that our computed solutions are better than human solutions decided by both non-professional and professional users.
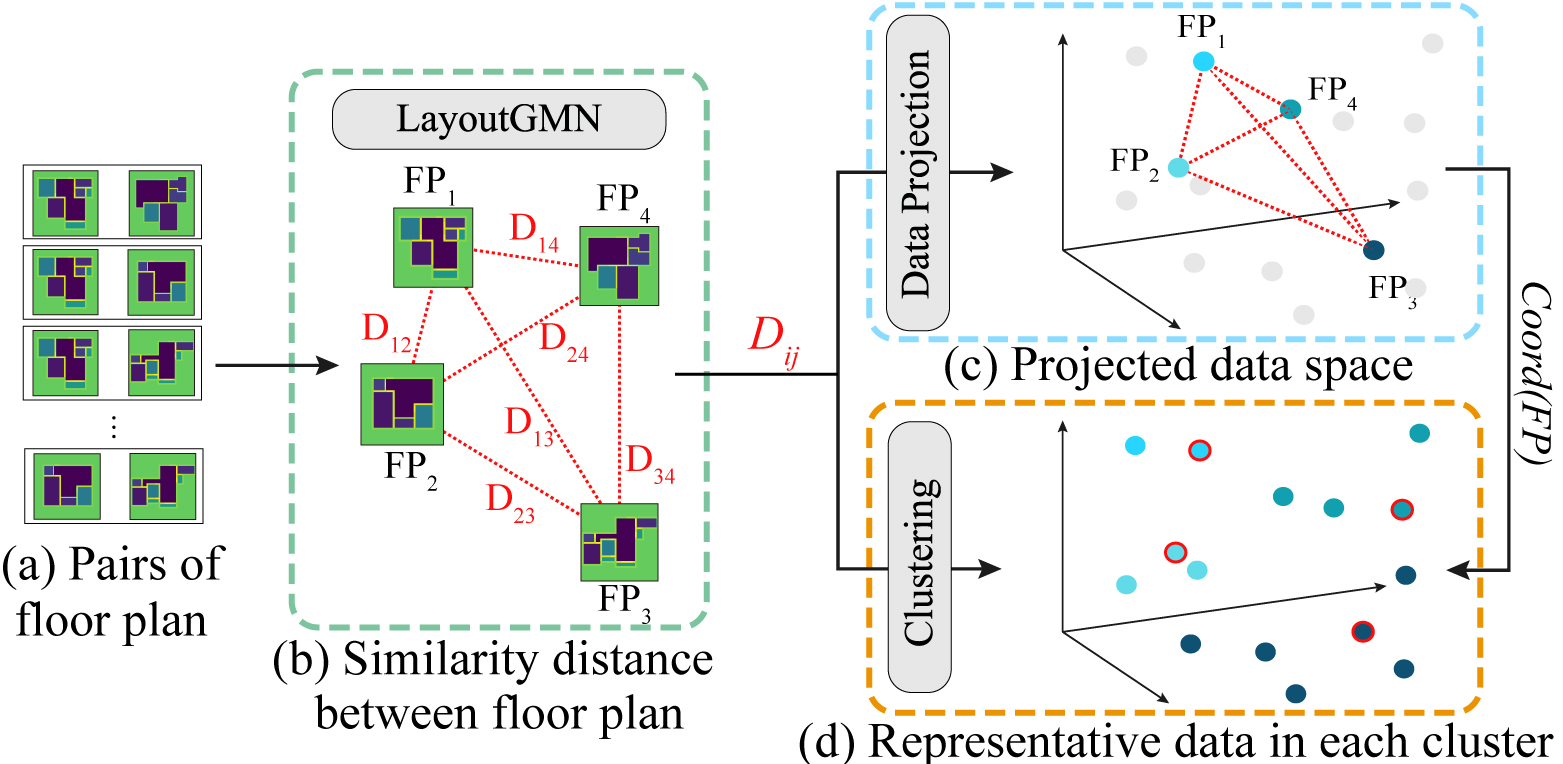
Floor Plan Exploration Framework Based on Similarity Distances
Chia-Ying Shih and Chi-Han Peng
Smart Tools and Applications in Graphics (STAG) (poster) 2022.
Paper | Arxiv |
Abstract:
Computational methods to compute similarities between floor plans can help architects explore floor plans in large datasets to avoid duplication of designs and to search for existing plans that satisfy their needs. Recently, LayoutGMN delivered state-of-the-art performance for computing similarity scores between floor plans. However, the high computational costs of LayoutGMN make it unsuitable for the aforementioned applications. In this paper, we significantly reduced the times needed to query results computed by LayoutGMN by projecting the floor plans into a common low-dimensional (e.g., three) data space. The projection is done by optimizing for coordinates of floor plans with Euclidean distances mimicking their similarity scores originally calculated by LayoutGMN. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations show that our results match the distributions of the original LayoutGMN similarity scores. User study shows that our similarity results largely match human expectations.
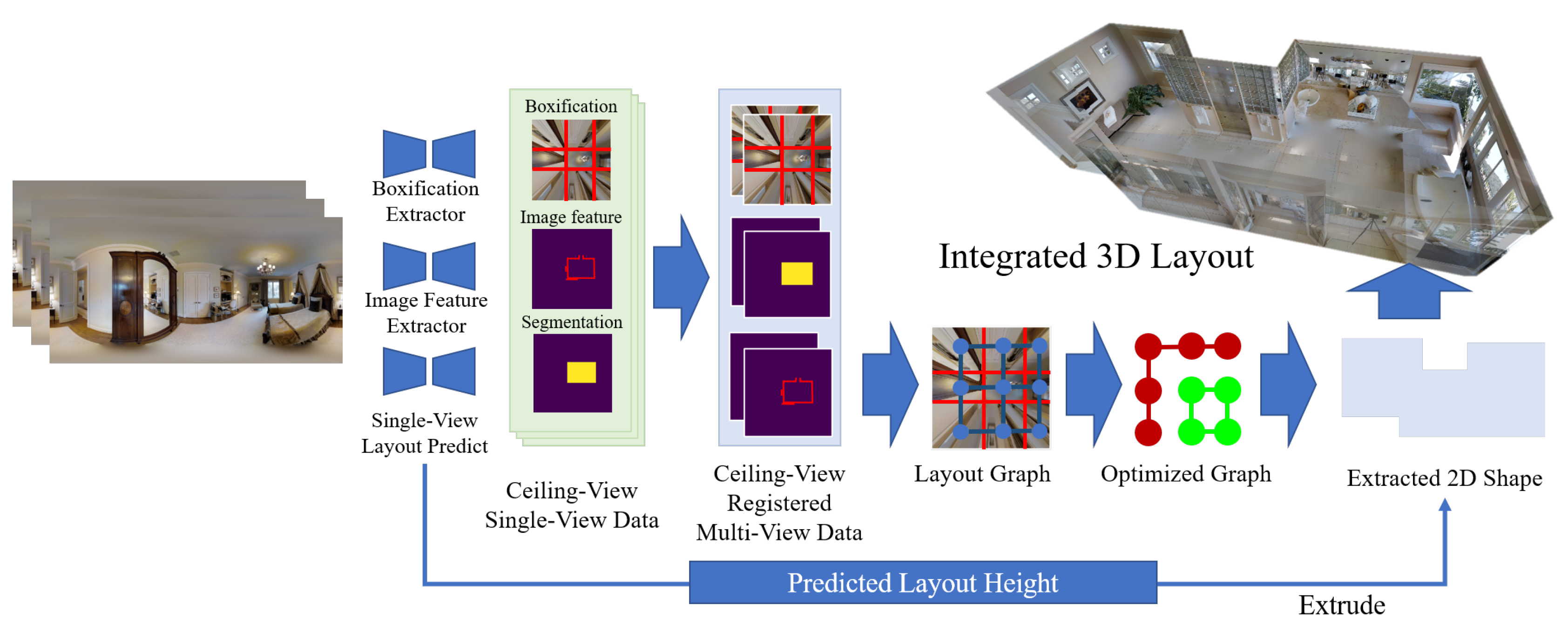
Reconstructing 3D Indoor Layout from Multiple Panoramic Images (結合深度學習與圖形最佳化方法之多視角室內全景影像三維格局重建)
Sio-Keong Si, Jheng-Wei Su, Chi-Han Peng, Kuo-Wei Chen, Felix Chang, Chih-Yuan Yao, and Hung-Kuo Chu
Computer Graphics Workshop (CGW), 2021 *Best Paper Award
Paper
Abstract:
We propose a novel framework to estimate room layouts from multiple panoramas taken inside the same room with registration. Our solution consists of the following major components. First, we propose a boxification line prediction network that can predict boxification lines for each panorama in the same room. Second, we propose a graph-cut based binary segmentation that produces room layouts with sharp corners and straight walls. Third, we also annotated one multi-view consistent layout dataset for this new layout prediction framework. Our quantitative results show an improvement over single-view room layout estimation algorithms.
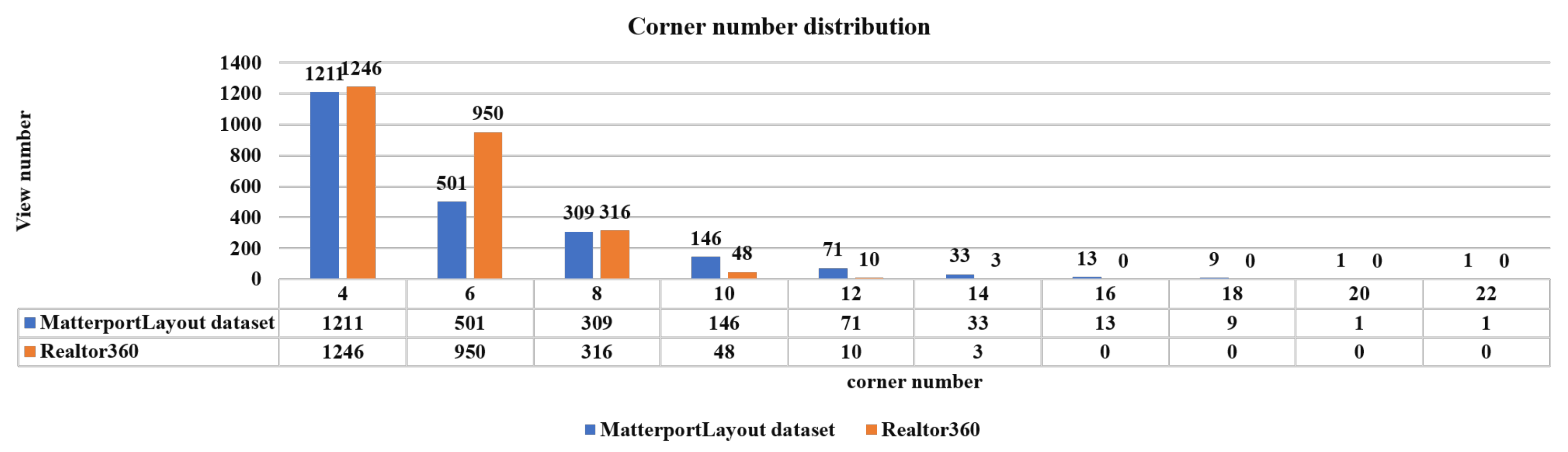
Manhattan Room Layout Reconstruction from a Single 360∘ Image: A Comparative Study of State-of-the-Art Methods
Chuhang Zou, Jheng-Wei Su, Chi-Han Peng, Alex Colburn, Qi Shan, Peter Wonka, Hung-Kuo Chu, and Derek Hoiem
International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), 2021
Paper (Preprint) |
Abstract:
Recent approaches for predicting layouts from 360◦ panoramas produce excellent results. These approaches build on a common framework consisting of three steps: a preprocessing step based on edge-based alignment, prediction of layout elements, and a post-processing step by fitting a 3D layout to the layout elements. Until now, it has been difficult to compare the methods due to multiple different design decisions, such as the encoding network (e.g., SegNet or ResNet), type of elements predicted (e.g., corners, wall/floor boundaries, or semantic segmentation), or method of fitting the 3D layout. To address this challenge, we summarize and describe the common framework, the variants, and the impact of the design decisions. For a complete evaluation, we also propose extended annotations for the Matterport3D dataset, and introduce two depth-based evaluation metrics.
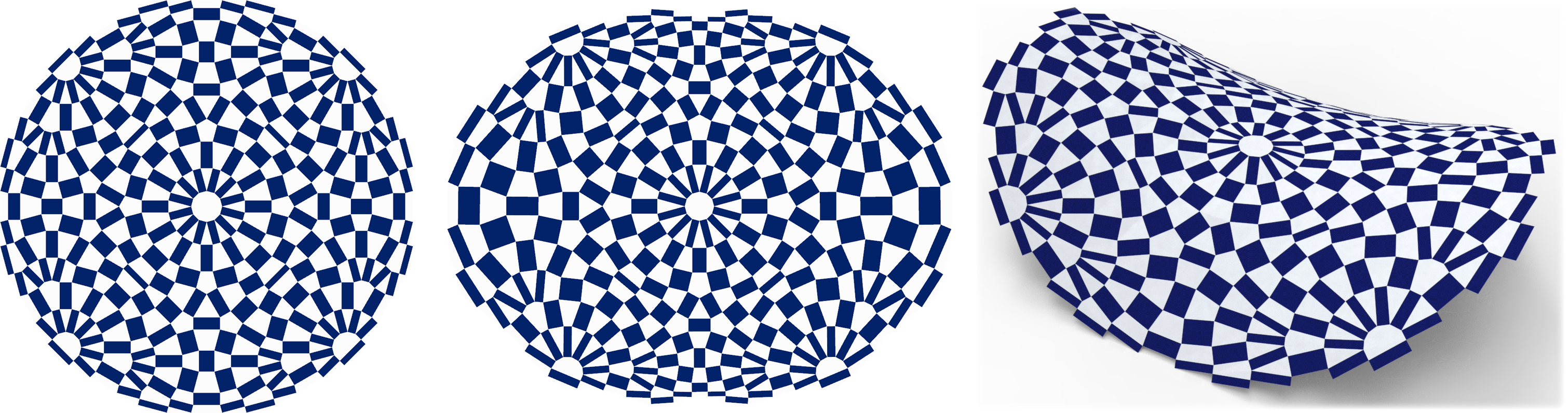
Checkerboard Patterns with Black Rectangles
Chi-Han Peng*, Caigui Jiang*, Peter Wonka, Helmut Pottmann
ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2019)
Paper | Additional Materials | Video |
Abstract:
Checkerboard patterns with black rectangles can be derived from quad meshes with orthogonal diagonals. First, we present an initial theoretical analysis of these quad meshes. The analysis reveals many possible applications in geometry processing and also motivates the numerical optimization for aesthetic and functional checkerboard pattern design. Second, we describe an optimization algorithm that transforms initial 2D and 3D quad meshes into quad meshes with orthogonal diagonals. Third, we present a 2D checkerboard pattern design framework based on integer programming inspired by the logo design of the 2020 Olympic games. Our results show a variety of 2D and 3D checkerboard patterns that can be derived from 2D or 3D quad meshes with orthogonal diagonals.
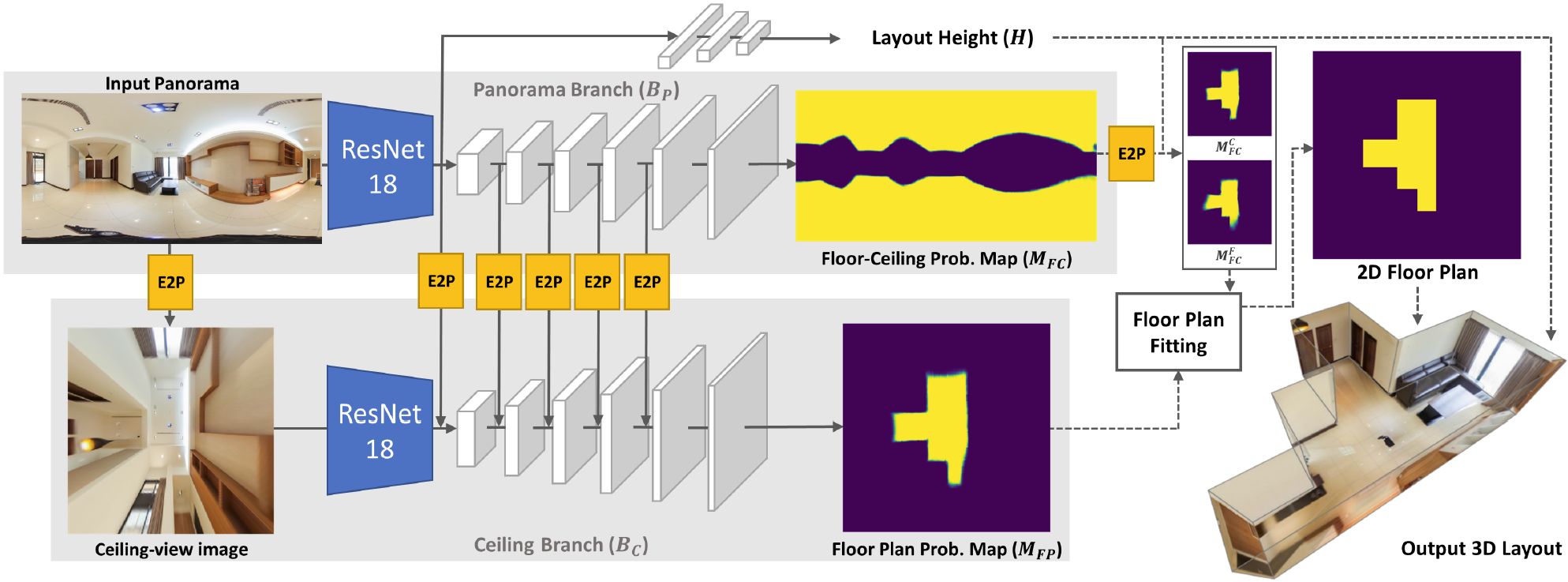
DuLa-Net: A Dual-Projection Network for Estimating Room Layouts from a Single RGB Panorama
Shang-Ta Yang, Fu-En Wang, Chi-Han Peng, Peter Wonka, Min Sun, Hung-Kuo Chu
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019
Paper (Arxiv) | Project | GitHub |
Abstract:
We present a deep learning framework, called DuLa-Net, to predict Manhattan-world 3D room layouts from a single RGB panorama. To achieve better prediction accuracy, our method leverages two projections of the panorama at once, namely the equirectangular panorama-view and the
perspective ceiling-view, that each contains different clues about the room layouts. Our network architecture consists of two encoder-decoder branches for analyzing each of the two views. In addition, a novel feature fusion structure is proposed to connect two branches, which are then jointly trained to predict the 2D floor plans and layout heights. To learn more complex room layouts, we introduce the Realtor360 dataset that contains panoramas of Manhattan world room layouts with different numbers of corners. Experimental results show that our work outperforms recent state-of-the-art in prediction accuracy and performance, especially in the rooms with non-cuboid layouts.
Designing Patterns using Triangle-Quad Hybrid Meshes
Chi-Han Peng, Helmut Pottmann, Peter Wonka
ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2018)
Paper | Additional Materials | Video | Models |
Abstract:
We present a framework to generate mesh patterns that consist of a hybrid of both triangles and quads. Given a 3D surface, the generated patterns fit the surface boundaries and curvatures. Such regular and nearly regular triangl-equad hybrid meshes provide two key advantages: first, novel-looking polygonal patterns achieved by mixing different arrangements of triangles and quads together; second, a finer discretization of angle deficits than utilizing triangles or quads alone. Users have controls over the generated patterns in global and local levels. We demonstrate applications of our approach in architectural geometry and pattern design on surfaces.
Computational Network Design from Functional Specifications
Chi-Han Peng, Yong-Liang Yang, Fan Bao, Daniel Fink, Dong-Ming Yan, Peter Wonka, Niloy J. Mitra
ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2016)
Paper | Slides |
Abstract:
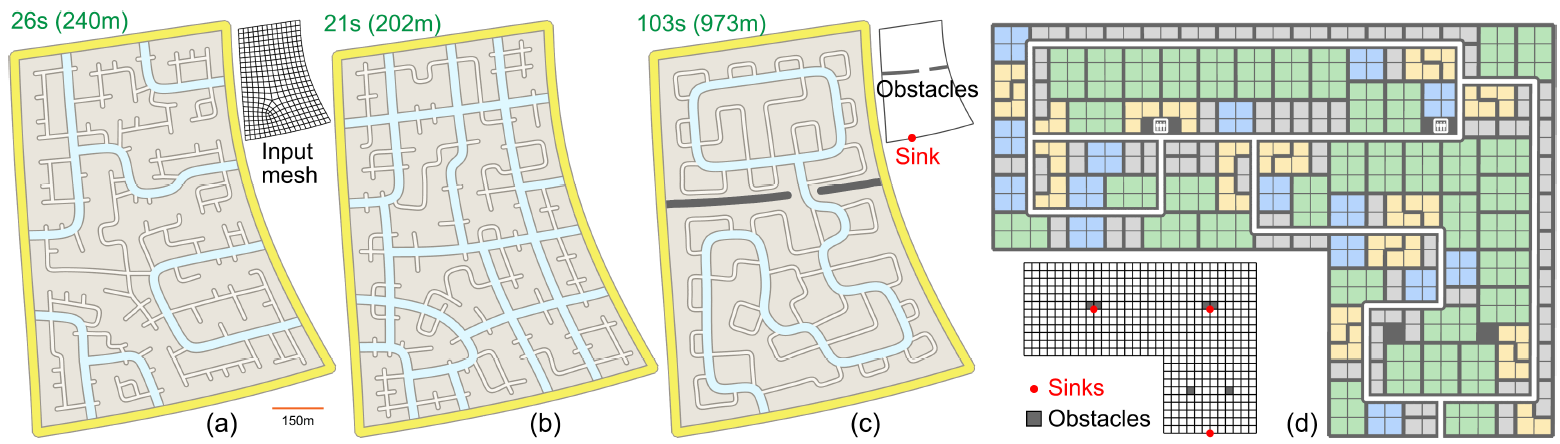
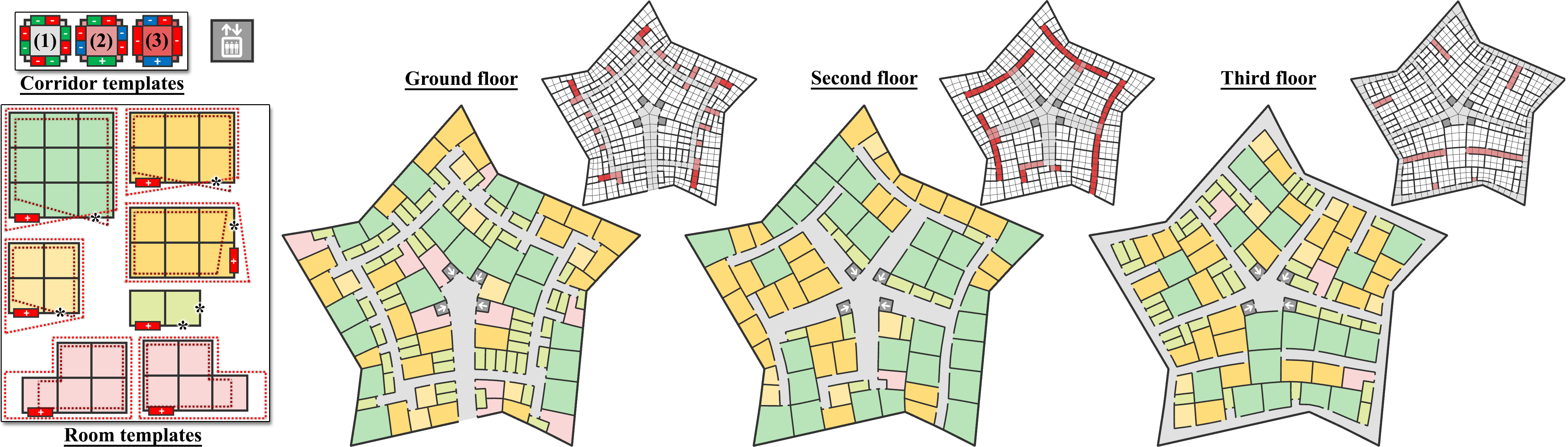
Connectivity and layout of underlying networks largely determine agent behavior and usage in many environments. For example, transportation networks determine the flow of traffic in a neighborhood, whereas building floorplans determine the flow of people in a workspace. Designing such networks from scratch is challenging as even local network changes can have large global effects. We investigate how to computationally create networks starting from only high-level functional specifications. Such specifications can be in the form of network density, travel time versus network length, traffic type, destination location, etc. We propose an integer programming-based approach that guarantees that the resultant networks are valid by fulfilling all the specified hard constraints and that they score favorably in terms of the objective function. We evaluate our algorithm in two different design settings, street layout and floorplans to demonstrate that diverse networks can emerge purely from high-level functional specifications.
Computing Layouts with Deformable Templates
Chi-Han Peng, Yong-Liang Yang, and Peter Wonka
ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2014)
Project Page | Paper | Additional Materials | Talk Slides | Fast-Forward Slides |
Abstract:
In this paper we tackle the problem of tiling a domain with a set of deformable templates. A valid solution to this problem completely covers the domain with templates such that the templates do not overlap. We generalize existing specialized solutions and formulate a general layout problem by modeling important constraints and admissible template deformations. Our main idea for the solution is to break the layout algorithm into two steps: a discrete step to layout the approximate template positions and a continuous step to refine the template shapes. Our approach is suitable for a large class of applications, including floorplanning, urban layouts, and arts and design.
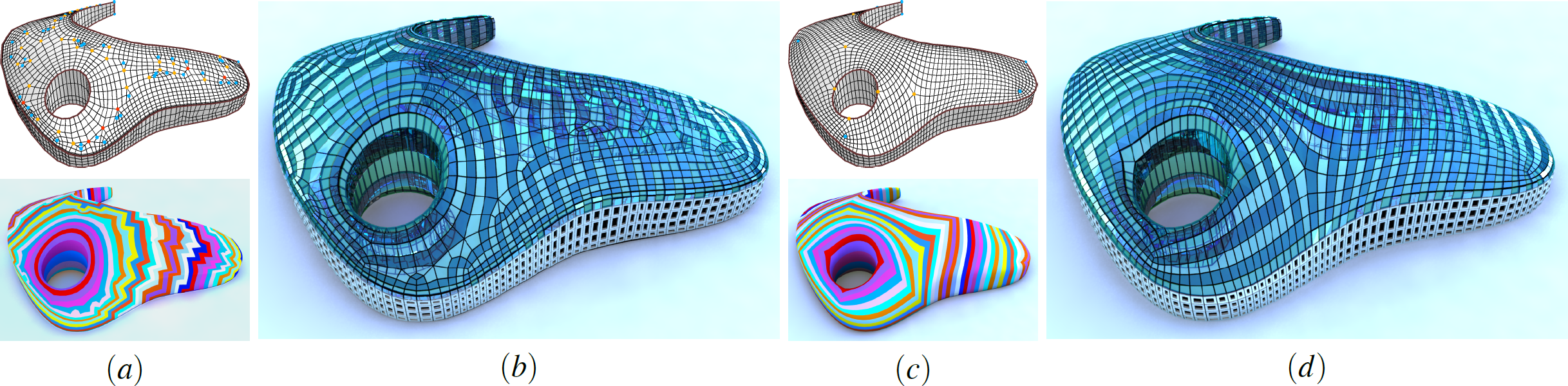
Exploring Quadrangulations
Chi-Han Peng, Michael Barton, Caigui Jiang, and Peter Wonka
ACM Transactions on Graphics (to be presented at SIGGRAPH 2014)
Project Page | Paper | Additional Materials | Video (youtube) | Models | Talk Slides | Fast-Forward Slides |
Abstract:
We present a framework for exploring topologically unique quadrangulations of an input shape. First, the input shape is segmented into surface patches. Second, different topologies are enumerated and explored in each patch. This is realized by an efficient subdivision-based quadrangulation algorithm that can exhaustively enumerate all mesh topologies within a patch. To help users navigate the potentially huge collection of variations, we propose tools to preview and arrange the results. Furthermore, the requirement that all patches need to be jointly quadrangulatable is formulated as a linear integer program. Finally, we apply the framework to shape-space exploration, remeshing, and design to underline the importance of topology exploration.
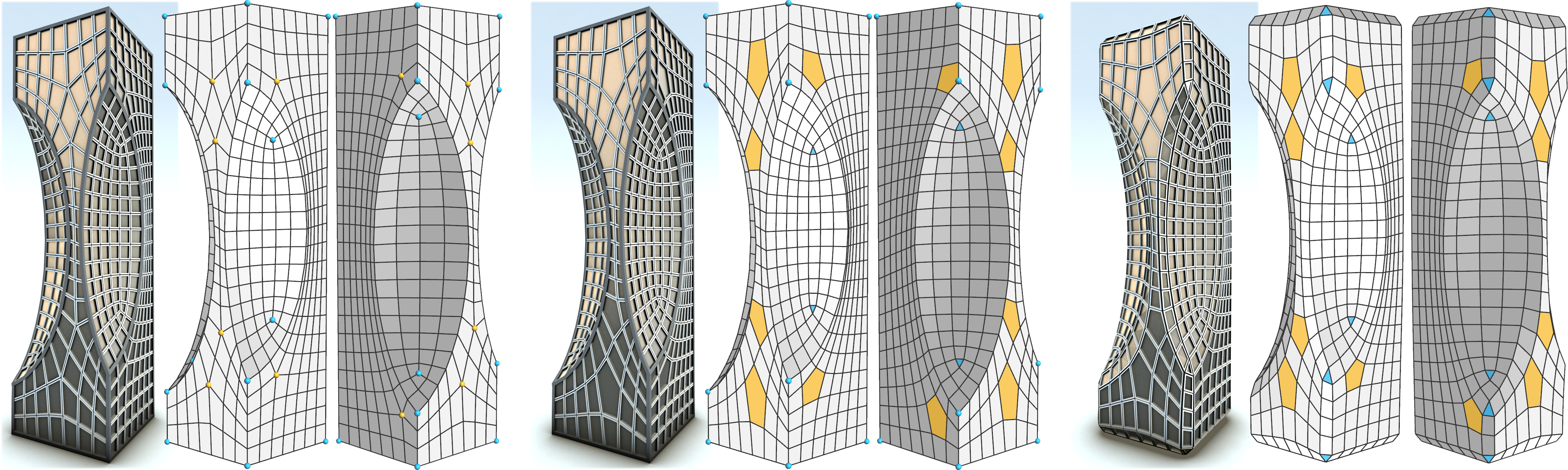
Connectivity Editing for Quad-Dominant Meshes
Chi-Han Peng and Peter Wonka
Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (SGP) 2013
Paper | Additional Materials | Video (youtube) | Slides |
Abstract:
We propose a connectivity editing framework for quad-dominant meshes. In our framework the user can edit the mesh connectivity to control the location, type, and number of irregular vertices (with more or less than four neighbors) and irregular faces (non-quads). We provide a theoretical analysis of the problem, discuss what edits are possible and impossible, and describe how to implement an editing framework that realizes all possible editing operations. In the results we show example edits and illustrate advantages and disadvantages of different strategies for quad-dominant mesh design.
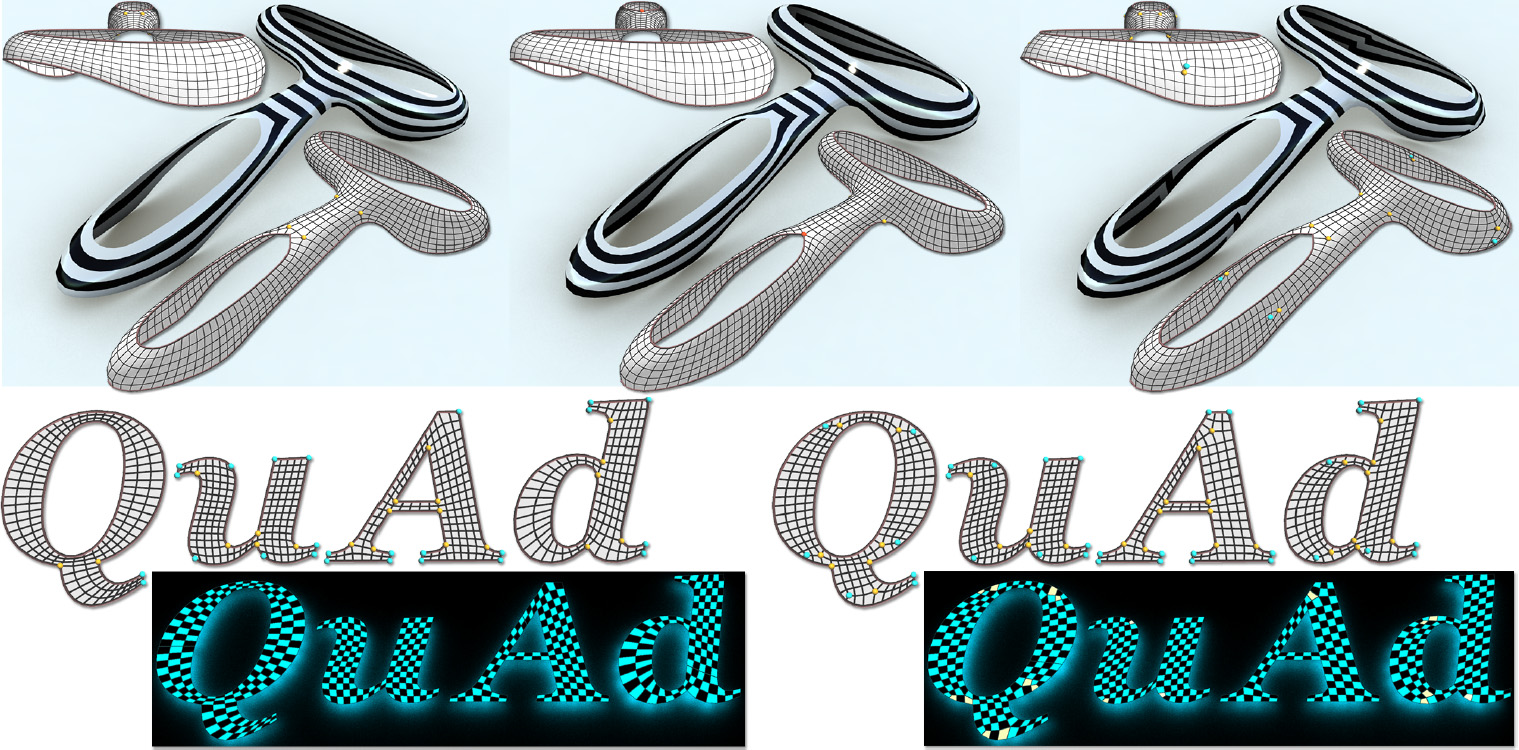
Connectivity Editing for Quadrilateral Meshes
Chi-Han Peng, Eugene Zhang, Yoshihiro Kobayashi, and Peter Wonka
ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2011)
Project Page | Paper | Additional Materials | Video (youtube) | Slides |
Abstract:
We propose new connectivity editing operations for quadrilateral meshes with the unique ability to explicitly control the location, orientation, type, and number of the irregular vertices (valence not equal to four) in the mesh while preserving sharp edges. We provide theoretical analysis on what editing operations are possible and impossible and introduce three fundamental operations to move and re-orient a pair of irregular vertices. We argue that our editing operations are fundamental, because they only change the quad mesh in the smallest possible region and involve the fewest irregular vertices (i.e., two). The irregular vertex movement operations are supplemented by operations for the splitting, merging, canceling, and aligning of irregular vertices. We explain how the proposed highlevel operations are realized through graph-level editing operations such as quad collapses, edge flips, and edge splits. The utility of these mesh editing operations are demonstrated by improving the connectivity of quad meshes generated from state-of-art quadrangulation techniques.
User-Assisted Mesh Simplification
Tan-Chi Ho, Yi-Chun Lin, Jung-Hong Chuang, Chi-Han Peng, Yu-Jung Cheng
VRCIA '06 Proceedings of the 2006 ACM international conference on Virtual reality continuum and its applications
Paper |
Abstract:
During the last decade, many simplification methods have been proposed to generate multi-resolution meshes for real-time applications. Practitioners have found that these methods alone usually fail to produce satisfactory result when models of very low polygon count are desired. This is due to the fact that the existing methods take no semantic or functional metric into account, and moreover, each error metric has its own strength and weakness. In this paper, we propose a user-assisted mesh simplification framework that allows users to improve the quality of simplified meshes derived by any error metric. The framework consists of two stages. The first stage employs a weighting scheme that allows users to refine a unsatisfactory region to achieve a user-specified resolution. The second stage is a local refinement scheme aiming to provide a user-guided fine-tune to recover local sharp features. The proposed weighting scheme differs from the previous approaches in that the weights are used to directly reorder the edge collapsing sequence rather than weighting the collapsing cost. Such a direct reordering mechanism ensures a predictable increase of resolution in the selected region, and is both error-metric and resolution independent.
Posters
Connectivity Control for Quad-Dominant Meshes with Applications in Urban Design
Chi-Han Peng
Advances in Architectural Geometry (AAG) 2014
Poster
Feature Detection in Aerial Images
Cheng Pan, Yifan Zhang, and Chi-Han Peng (Advisers: John Femiani, Anshuman Razdan, and Peter Wonka)
SIAM Data Mining Conference (SDM) 2011 Doctoral Forum
Poster